An overview
Anthropology and Archeology are two interrelated disciplines that deal with
the origin and development of human culture and hence occupy an important
Place in social sciences prehistory,protohistory and civilization are an integral part which needs to be understood in both the disciplines.
read mini article at https://medium.com/@hoboknowledge/anthropology-4af7ee3cff27
Anthropology basically deals with the study of present-day-simple societies and it has two main divisions called physical anthropology and social anthropology. Several branches within it developed in the course of time like cultural anthropology, etc. Archeology endeavors to reconstruct ancient societies and is treated as part of anthropology in American universities.The mutual interdependence of anthropology and archeology arises from the simple fact that both deals with the study of human cultures-one of the present and the Other of the past.
Archeological anthropology is one of the sub branches of anthropology
deals with the origin and development of human species and its material
Manifestations in the form of material culture. Archeology not only helps
us to understand diversity in the world around us,but also to understand
How people relate to the material world.
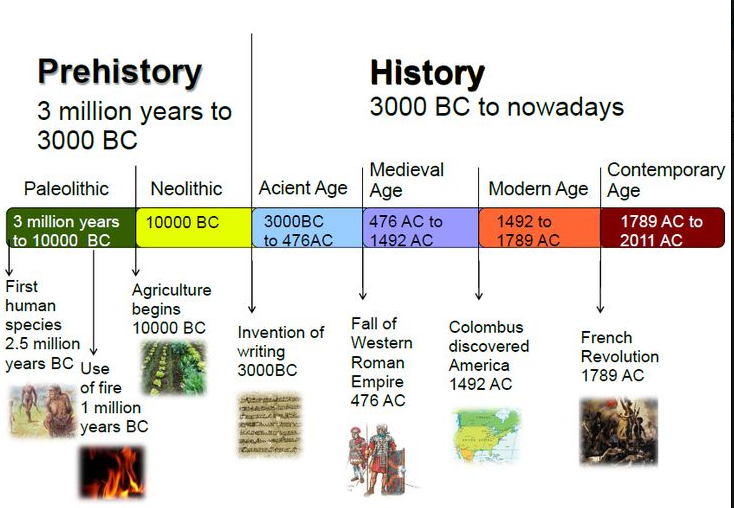
PREHISTORY

Throughout this period man led a nomadic way of life with hunting of wild animals and gathering of wild plant foods as the chief mode of subsistence. Technology was based on the preparation of tools on a variety of rocks like quartzite and even limestone and siliceous stones like chert and jasper. Depending upon improvements in tool making traditions and to some extent, changes in hunting-foraging methods, prehistoric period is divided into three major phases or stages called the Lower, Middle and Upper Palaeolithic.
All these three stages are dated to the geological period called Pleistocene. In the
early part of the Holocene tiny stone implements called microlith came into
Vogue. This stage is called the Mesolithic. In addition to stone, wood and bone
also began to be used for making tools from the Middle and Upper Paleolithic
Phases.
Throughout this period man led a nomadic way of life with hunting of wild animals and gathering of wild plant foods as the chief mode of subsistence. Technology was based on the preparation of tools on a variety of rocks like quartzite and even limestone and siliceous stones like chert and jasper. Depending upon improvements in tool making traditions and to some extent, changes in hunting-foraging methods, prehistoric period is divided into three major phases or stages called the Lower, Middle and Upper Palaeolithic.
All these three stages are dated to the geological period called Pleistocene. In the
early part of the Holocene tiny stone implements called microlith came into
Vogue. This stage is called the Mesolithic. In addition to stone, wood and bone
also began to be used for making tools from the Middle and Upper Paleolithic
Phases.

Prehistoric stone tools are grouped into two broad categories: tools for heavy
Work (heavy duty tools) and tools for light work (light duty tools). These were
used for a variety of operations such as hunting, digging of roots and tubers,
cutting, scraping, fensing and boring connected with the acquisition, processing
And consumption of animal and plant foods.
The Lower Paleolithic stage is characterized by large sized tools such as
hand axes, cleavers, chopping tools, polyhedrons, etc. The Middle Paleolithic
tools are smaller in size and consist of flake – tools such as scrapers, points and
borers etc. The Upper Paleolithic culture belongs to Late Pleistocene and is
characterized by blade technology leading to the production of long, slender looking backed blades, points, penknives, saw edged blades, etc. In the succeeding
Mesolithic tools become very small or tiny in size, generally measuring a few
Centimeters in length. The types include backed blades, lunate, triangles, points,
etc., all used to prepare composite implements such as arrowheads, spearheads
and harpoons. Rock art and intentional burial of the dead also come into vogue in the Mesolithic stage.
PROTOHISTORY
The term ‘la Protohistorique,’ was first coined by the French, to refer to a period
Transposed between prehistory and true historical Period. It suits India very well.
First, before historical period there is evidence of writing in the Harappa or
Indus valley scripts, though as yet undecipherable. Secondly, though the Vedic
literature was in an oral state up to the 4th century AD or so, its antiquity goes
back to the second millennium B.C.
What has been archived by Archeological survey of India since its inception in 1902 in the field of proto historic archeological is most remarkable indeed.